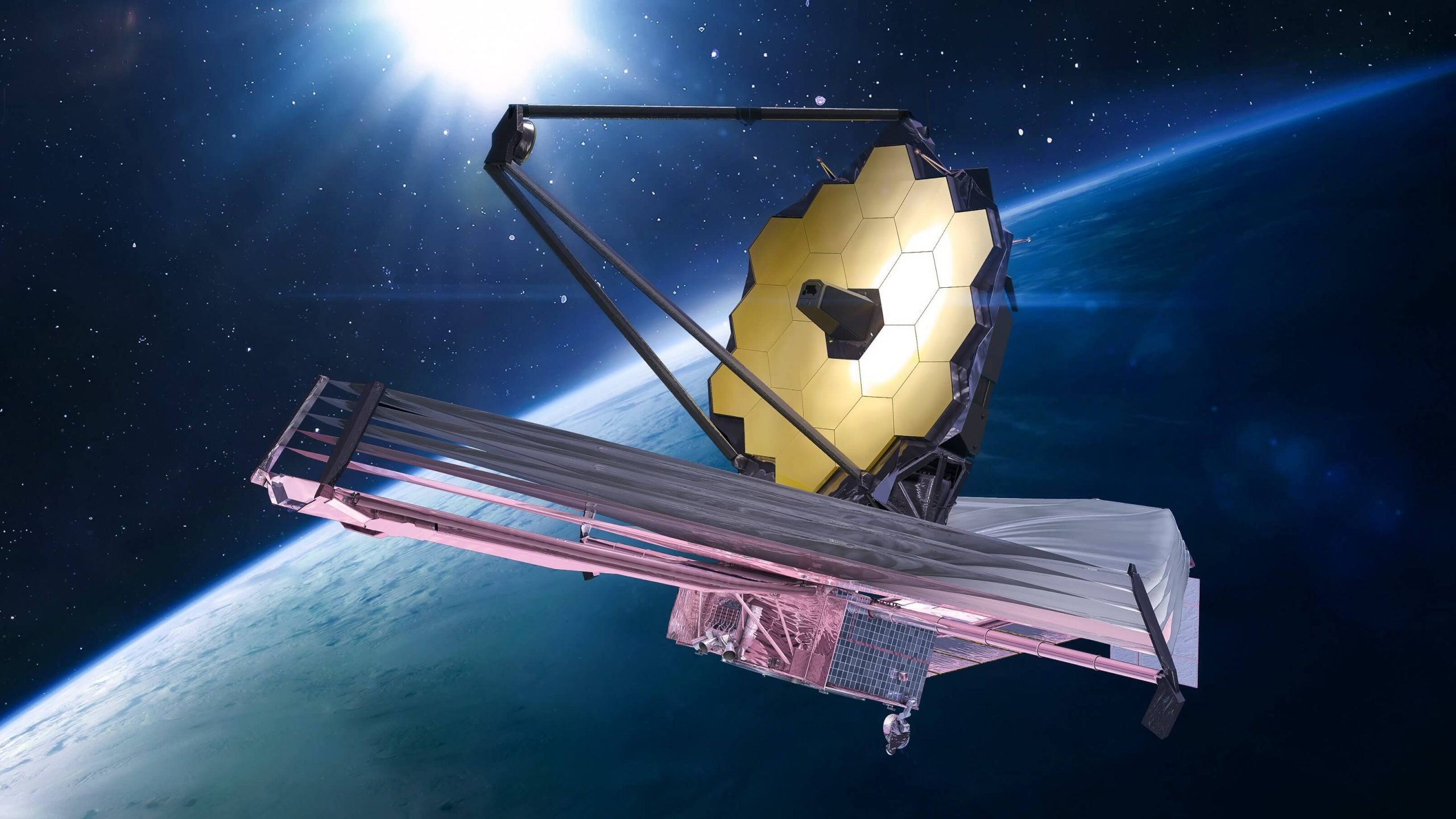
The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is a large optical telescope which has been launched into space and is now conducting astronomy operations in space. This telescope has a large sensitivity and resolution and is able to view objects that the Hubble Space Telescope cannot see.
James Webb Space Telescope Design and Capabilities
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space-based observatory that will offer a new and detailed view of the universe. It will be able to observe the birth of stars, black holes, and planets, as well as the atmospheres of exoplanets.
The JWST is scheduled to launch in October. Unlike the Hubble telescope, which works only in visible light, Webb will operate in infrared wavelengths. This will allow scientists to study cooler gases around black holes and the atmospheres of extrasolar planets.
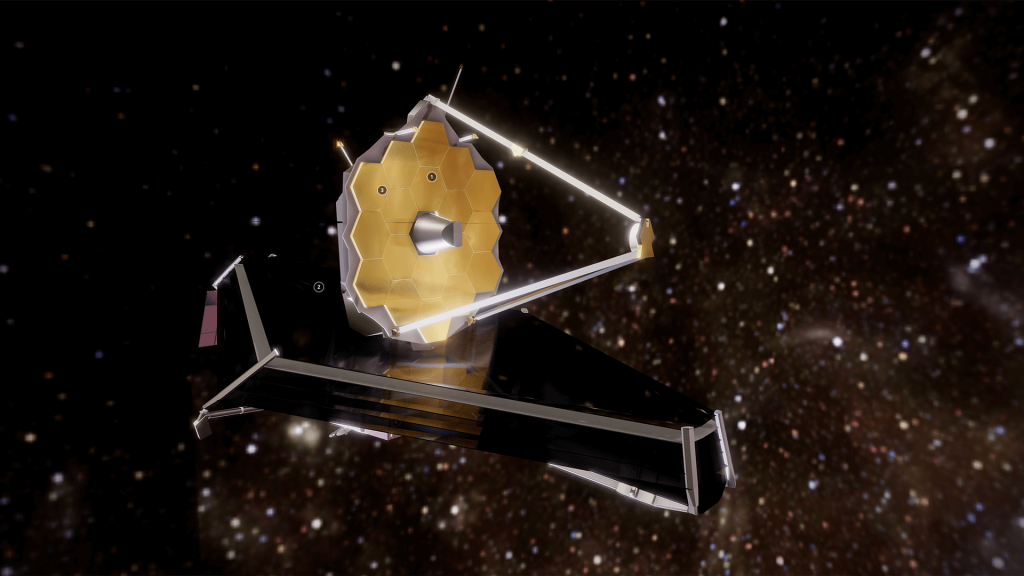
For this mission, the Webb telescope is designed to be 100 times more sensitive than the Hubble. The telescope is also much larger. When it’s finally finished, the telescope will have a mirror that’s 21.3 feet wide.
One of the main challenges of building a telescope that’s as large as Webb is that the components must undergo an exhaustive gauntlet of testing. As the assembly continues, the strain on the components will increase.
The JWST’s primary mirror has a hexagonal shape. This is ideal for focusing light for imaging. Because the primary mirror is made of beryllium, it’s light-weight and strong. In addition, beryllium is highly polished to provide high accuracy.
The Webb telescope has 18 hexagonal mirror segments. Each of these segments has about 269 square feet of effective area.
Scientific Objectives
The James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) will be one of the most powerful and sensitive space telescopes in the universe. It will be used to study the history and structure of the universe and the formation of planets, stars and quasars.
In addition to its primary focus, Webb will also search for signs of life on exoplanets, or planets outside of our solar system.
As the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, the Webb telescope will be an advanced optical system. Compared to Hubble, the Webb telescope is expected to have a 100-fold increase in sensitivity. This will give it the ability to detect and analyze the atmospheres of extrasolar planets.

Webb’s mirrors will be made of hexagonal segments, each of which will be controlled by six actuators. Using these actuators, the segments will meld together into one single, also it is curved optical surface.
The Webb telescope is a partnership between NASA and the European and Canadian Space Agencies. They are collaborating on the project, and each is providing their expertise to help build the instrument.
The James Webb Space Telescope will be launched in 2021. It will orbit the sun and study the earliest light in the early universe, as well as the formation and evolution of galaxies, quasars and other stellar objects.
Launch and Deployment
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is one of the world’s most powerful and advanced space observatories. It’s able to peer deep into the cosmos, providing a window into the history and evolution of our universe.
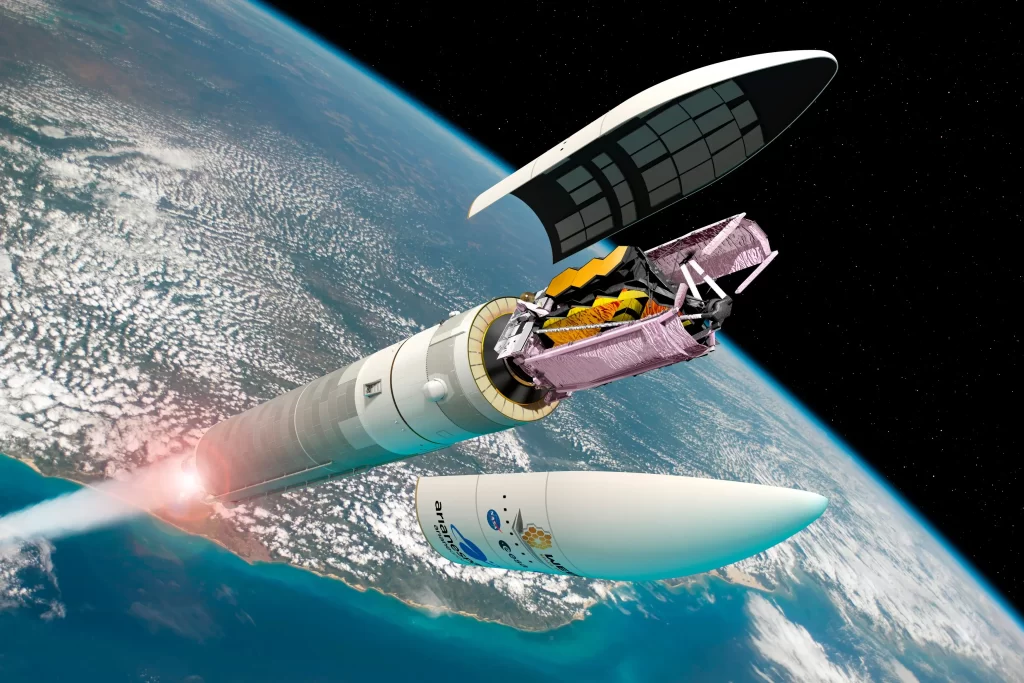
The telescope was launched on December 25, 2021, on board an Ariane 5 rocket from Guiana Space Center in French Guiana. At 12:20 UTC on the launch date, the rocket lifted off. Webb’s solar array was deployed and its high rate antenna became operational, providing a connection with the Earth.

Although Webb’s main function is to take pictures, it also has a number of instruments designed to detect infrared radiation. The instrument is sensitive to colors that are not visible to the human eye, and the team is working to calibrate the instrument to its optimal levels.
The first mid-course correction burn was performed 12 hours after launch. This burn corrected the trajectory of the telescope and set it on the right course for the rest of its mission. Another burn is scheduled for T+2 days.
There’s a lot of work left to do, but the first images should start arriving in early April. After that, Webb will begin routine science operations. These include mapping the sky and identifying exoplanets. By the time it’s finished, the observatory should have a lifetime of about 10 years.
You can reach the official website of NASA by clicking here.
Or read more news contents.





