Scientists Uncover the Mechanism Behind High Contrast Optical Illusions
Researchers from the University of Exeter have made a breakthrough in understanding high contrast optical illusions, shedding light on why these images trick our eyes. Contrary to previous assumptions about the involvement of complex neurological processes.
The study suggests that limitations in the human eye’s visual system are responsible for these illusions. The findings challenge long-held beliefs and offer valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying visual perception.
In the study published in PLOS Computational Biology, researchers discovered that high contrast optical illusions exploit limitations in the eye’s visual system rather than relying on the brain’s processing power.
Dr. Jolyon Troscianko, one of the authors, explained that the neurons in our eyes have a finite firing capacity. Which affects our perception of color and contrast.
The Role of Neuron Bandwidth in High Contrast Optical Illusions
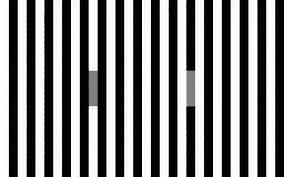
The researchers developed a computer model that replicated the limited bandwidth of human vision. When exposed to high contrast optical illusions, the model became overwhelmed by the presence of significant contrasts. Leading to distorted perceptions of the images.
The model revealed that different neurons have evolved to be finely tuned at processing subtle variations in color across a range of shades.
Neurons sensitive to small differences in gray levels at medium-sized ranges are easily overwhelmed by high contrasts.
In contrast, neurons coding for contrasts at larger or smaller scales are less sensitive. But can handle a wider range of contrasts, creating distinct black-and-white differences.
The computer model created in this study opens up avenues for further exploration. Scientists aim to use the model to study color perception in animals with different visual systems. Ad neuron bandwidths compared to humans.
By understanding how different species perceive color. Researchers can gain valuable insights into the diversity of visual experiences across the animal kingdom.
The University of Exeter’s study provides a breakthrough in understanding the mechanisms behind high contrast optical illusions.
By demonstrating that these illusions exploit limitations in the eye’s visual system rather than complex neurological processes, the research challenges long-held assumptions.
The computer model developed in the study sheds light on the role of different neurons and their sensitivity to contrasts at varying scales.
This research paves the way for further investigations into color perception in different species and expands our understanding of visual experiences beyond human perception.
Are Optical Illusions Bad for Your Eyes?
Optical illusions captivate our attention by playing tricks on our minds making us perceive things differently, than their form. It’s worth noting that these illusions are not inherently harmful to our eyes.
Instead they cleverly exploit how our visual system processes information resulting in captivating effects. However it’s essential to be mindful of prolonged exposure to patterns or flickering images as they can potentially cause eye strain or discomfort for some individuals.
To ensure an experience it is advisable to indulge in illusions moderately and take breaks if any discomfort arises. Generally speaking the average person need not worry about term impacts, on their eye health when enjoying optical illusions.
Are Optical Illusions Dangerous?
Optical illusions pose no danger. They offer methods to explore the intricacies of our perception, commonly employed in psychological and neurological research.
Nonetheless individuals, with health conditions like epilepsy need to exercise caution when exposed to types of optical illusions featuring rapid light changes or intense visual patterns as these may potentially provoke seizures.
However, for the majority of people optical illusions are completely safe. Serve as enjoyable forms of entertainment or educational tools that shed light on the fascinating complexities of human perception and brain function.





