The Difference Between Step Index And Graded Index
Optical fibers play a role, in communication by providing efficient and fast data transmission across long distances. Step index and graded index fibers among the types are particularly noteworthy due, to their distinct characteristics and wide range of applications. This post delves into these two types, highlighting the difference between step index and graded index fiber in various aspects.
Table of contents
- What is Step Index Fiber?
- What is Graded Index Fiber?
- What are the Advantages of Graded Index Fiber?
- Graded Index Fiber Formula
- What is Multimode Graded Index Fiber?
- Graded Index Fiber Structure
- Graded Index Fiber Diagram
- Graded Index Fiber Applications
- What is the FOA Graded-Index?
- How Does a Graded Index Work?
- How Do You Make Graded-Index Fiber?
- Is a Graded-Index Fiber Parabolic?
- Difference between Step Index and Graded Index Fiber
- Final Thought
What is Step Index Fiber?
Step index fiber is a kind of fiber that has a core and cladding with different refractive indices. The core, usually made of glass or plastic has a index while the cladding has a lower one. This contrast forms a boundary or “step,” which enables light to be guided through the core by internal reflection. Step index fibers are commonly used in applications due, to their straightforward design.
Step Index Fiber Definition
In the realm of fibers, a step index fiber is characterized as a fiber that possesses a core and cladding with contrasting refractive indices. This configuration leads to a transition, at the boundary between the core and cladding effectively directing light predominantly through the core. Such fibers play a role in communications by providing a direct method, for transmitting light.
Step Index Fiber Diagram
A typical illustration of a step index fiber displays a core that is encompassed by cladding. The core, responsible, for transmitting light is depicted as having a index while the cladding is represented with a lower refractive index. This distinction is often visualized using shades or colors to depict the “step” in index at the boundary, between the core and cladding.
What is Multimode Step Index Fiber?
Multimode step index fiber is a type of step index fiber that enables the transmission of light, through the core along modes or paths. These fibers possess a core diameter, which facilitates light to travel through paths. However this can result in dispersion impacting the bandwidth and transmission distance capabilities of the fiber, for data transmission.
What is Single Mode Step Index Fiber?
Single mode step index fiber on the hand has a core diameter, which enables the straight propagation of only one light mode through the fiber. This particular design helps reduce dispersion and’s highly suitable, for long distance communication and high bandwidth applications. Single mode step index fibers play a role, in telecommunications and data networks that demand data rates and minimal signal degradation.
What is Step Index Optical Fiber?
Step index optical fiber is a kind of fiber that has a core and cladding with refractive indices. This specific design, which has a distinction, between the core and cladding plays a role, in efficiently guiding light. Step index optical fibers have applications ranging from data transmission to intricate communication systems.
Step Index Fiber Formula
The functionality of a step index fiber can be comprehended by examining its formula, which usually incorporates the indices of the core and cladding (n1 and n2 respectively). By analyzing these indices we can determine the angle, for internal reflection as well, as the numerical aperture (NA) which gives us a better understanding of how effectively the fiber transmits light.
Step Index Fiber Numerical Aperture
The numerical aperture (NA) plays a role, in determining the acceptance capability of a step index fiber. It is determined by considering the indices of both the core and cladding. A higher NA signifies a capacity to capture light. It can also result in increased dispersion, which can impact the fibers performance during data transmission.
What are the Advantages of Step-Index Fibers?
Step index fibers offer benefits. One advantage is their design and cost effective manufacturing process. They are also easier to splice and handle compared to types of fibers. In area networks multimode step index fibers excel at transmitting light signals simultaneously over short distances. However, for long distance communication their usage is limited due, to dispersion and attenuation when compared to graded index fibers.
What is Step Index Fiber Simple?
Simply put a step index fiber is a fiber that consists of a core and a cladding. The core carries light while the cladding has a index. This particular design forms a boundary that reflects light back, into the core enabling transmission of light over long distances. It’s a efficient technology, in the field of fiber optics.
What is Graded Index Fiber?
Graded index fiber refers to a fiber in which the refractive index of the core gradually decreases from the center, towards the cladding. Unlike step index fibers, which have a boundary this gradual change reduces dispersion by allowing light rays to follow a curved path. As a result data transmission becomes more efficient, over distances.
What are the Advantages of Graded Index Fiber?
Graded index fiber offers benefits, over step index fibers. It reduces dispersion. Provides a higher bandwidth making it an excellent choice for medium, to long distance communication. These fibers can transmit data at rates while minimizing signal loss. Moreover their design enables utilization of light paths thereby enhancing the overall performance of fiber optic networks.
Graded Index Fiber Formula
The performance of graded index fiber is commonly explained using a formula that considers the index profile of the core. This profile usually takes the shape of a curve gradually decreasing from the center to the cladding. Having a grasp of this formula enables us to analyze how light propagates through the fiber and how effectively it reduces dispersion.
What is Multimode Graded Index Fiber?
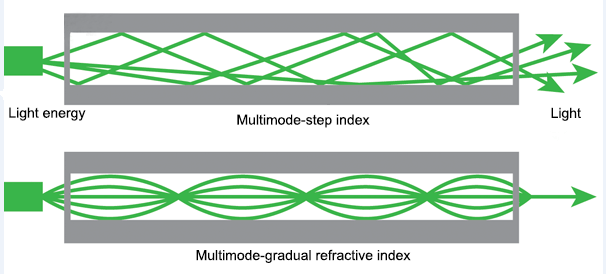
Multimode graded index fiber permits the transmission of light modes. It effectively reduces the issue of modal dispersion compared to multimode step index fibers. The graded refractive index profile allows light rays to follow a sinusoidal trajectory, which equalizes the travel time, for modes and enhances signal quality, over extended distances.
Graded Index Fiber Structure
A graded index fiber is made up of a core that has an index which gradually decreases as it moves towards the outer cladding. This particular design helps to minimize the dispersion of pulses over distances ensuring that high speed data transmission maintains its signal integrity.
Graded Index Fiber Diagram
A typical illustration of a graded index fiber displays a core that has an index gradually changing, depicted by a gradient or varying shades. This stands in contrast, to the core of a step index fiber visually demonstrating the methods used to control the propagation of light within the fiber.
Graded Index Fiber Applications
Graded index fibers find use in the telecommunications and data network industry, where maintaining data rates and minimizing signal loss over medium to long distances is of utmost importance. These fibers are well suited for applications such, as fiber to the home (FTTH) high speed internet backbones and data centers due, to their capability to reduce dispersion.
What is the FOA Graded-Index?
The term “FOA (Fiber Optic Association) graded index” pertains to a established standard or specification, for graded index fibers as defined by the Fiber Optic Association. This particular standard outlines the characteristics, performance criteria and application areas of graded index fibers serving as a reference, for industry purposes and ensuring quality assurance.
How Does a Graded Index Work?
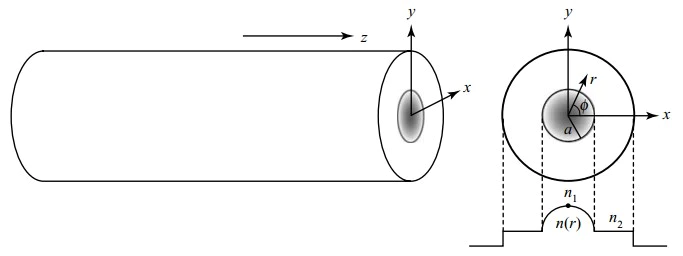
A graded index fiber operates based on the concept of index variation, within the core of the fiber. Unlike a step index fiber, where the core has a index a graded index fiber showcases a gradual change in the refractive index from the center to the outer edges. Typically this change follows a pattern. When light rays travel through the core of a graded index fiber they take on a curved path, than moving in lines or sharp bends.
This specific design helps reduce dispersion caused by varying path lengths of rays ultimately resulting in more efficient data transmission over longer distances. The difference between step index and graded index fiber lies in this unique refractive index profile, which significantly impacts performance and application.
How Do You Make Graded-Index Fiber?
The production of graded index fiber involves a procedure to achieve a change, in the refractive index. This is typically accomplished through two methods; Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition (MCVD) or Outside Vapor Deposition (OVD). In these processes layers of glass with compositions are deposited either inside or outside a substrate tube.
By adjusting the concentration of dopants such as germania the refractive index can be modified. The tube is then compressed into a rod. Subsequently drawn into a fiber. The precise control, over concentration leads to the parabolic index profile found in graded index fibers. This process is a key aspect in understanding the difference between step index and graded index fiber.
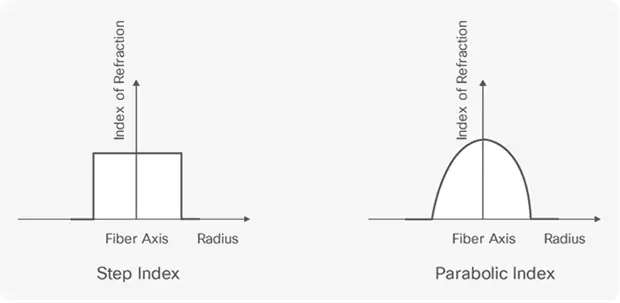
Is a Graded-Index Fiber Parabolic?
Indeed a graded index fiber generally features an index profile that resembles a shape. In terms the refractive index gradually decreases from the center of the fiber, towards its edge. This particular distribution enables rays to bend in a manner, towards the axis effectively minimizing modal dispersion.
The parabolic profile is crucial in maintaining signal integrity over longer distances, which is a significant difference between step index and graded index fiber. On the hand a step index fiber undergoes a shift, in refractive index at the boundary, between the core and cladding resulting in distinct characteristics for how light travels.
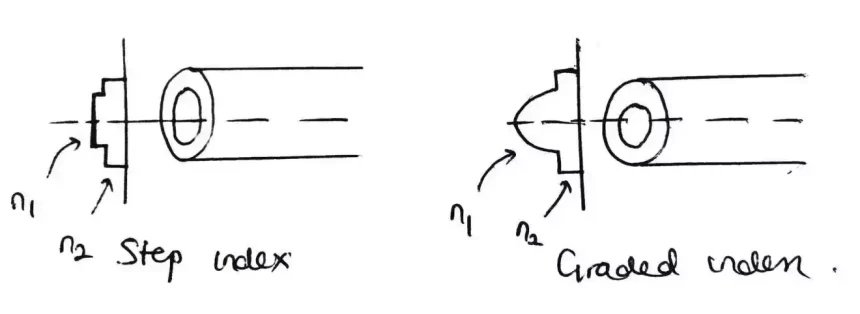
Difference between Step Index and Graded Index Fiber
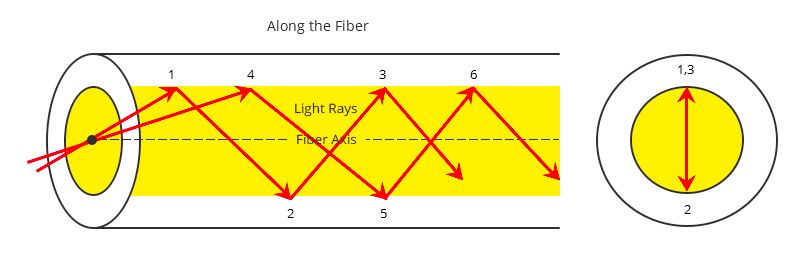
The difference between step index and graded index fiber is primarily in their refractive index profiles and the resulting light propagation methods. Step index fibers have a core, with a index resulting in a clear distinction from the cladding. This causes light to travel in a zigzag pattern due to reflection.
On the hand graded index fibers have an index that gradually changes, creating a parabolic profile. This design minimizes modal dispersion as light rays follow a trajectory. As a result graded index fibers generally provide improved bandwidth and are more efficient, for long distance communication compared to step index fibers.
Difference between Step Index and Graded Index Fibers
When discussing the difference between step index and graded index fibers, it’s important to consider their applications and performance. Step index fibers are less expensive and easier to produce, due to their structure. However they have a drawback of dispersion, which limits their bandwidth and effective distance. These fibers are commonly used for shorter distance applications.
On the hand graded index fibers have an intricate refractive index profile resulting in higher bandwidth capability. They are better suited for medium to long distance telecommunications. The reduced modal dispersion in graded index fibers enables data transmission making them the preferred choice, for high speed data networks.
Difference between Step Index and Graded Index Fiber in Tabular Form
| Feature | Step Index Fiber | Graded Index Fiber |
| Refractive Index Profile | Uniform throughout the core | Gradually changes, typically parabolic |
| Light Propagation | Zigzag path due to total internal reflection | Smooth, curved path reducing modal dispersion |
| Bandwidth | Lower due to higher modal dispersion | Higher, suitable for broadband applications |
| Manufacturing Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to complex manufacturing process |
| Application | Short-distance communication, simple systems | Medium to long-distance telecommunications, high-speed networks |
This table succinctly encapsulates the difference between step index and graded index fiber, highlighting their distinct characteristics and applications.
Difference between Step Index and Graded Index with Diagram
To visually represent the difference between step index and graded index fiber, a diagram can be highly effective. Imagine two diagrams side by side. The first image shows a type of fiber optic cable called a step index fiber. In this type of fiber there is a boundary, between the core and the outer cladding. The light rays are depicted as moving in zigzag patterns within the core.
On the hand the second diagram illustrates a kind of fiber called a graded index fiber. In this type the refractive index gradually decreases from the center to the edge of the core. As a result the light rays curve in patterns following an index profile.
These visual representations not highlight the structural disparities between step index and graded index fibers but also clearly demonstrate how light travels differently through them. This distinction plays a role, in understanding these two types of fibers.
Final Thought
The difference between step index and graded index fiber is a cornerstone in fiber optics, guiding the evolution of communication technologies. Different types of fibers have characteristics that impact their performance in telecommunications.
Short range step index fibers are simple. Limited in their capabilities while graded index fibers excel at long distance communication. These differences play a role, in shaping telecommunications affecting internet speeds and data reliability. To fully leverage the potential of communications it is important to understand and appreciate these distinctions as we continue to advance and connect our world.
You May Also Like





